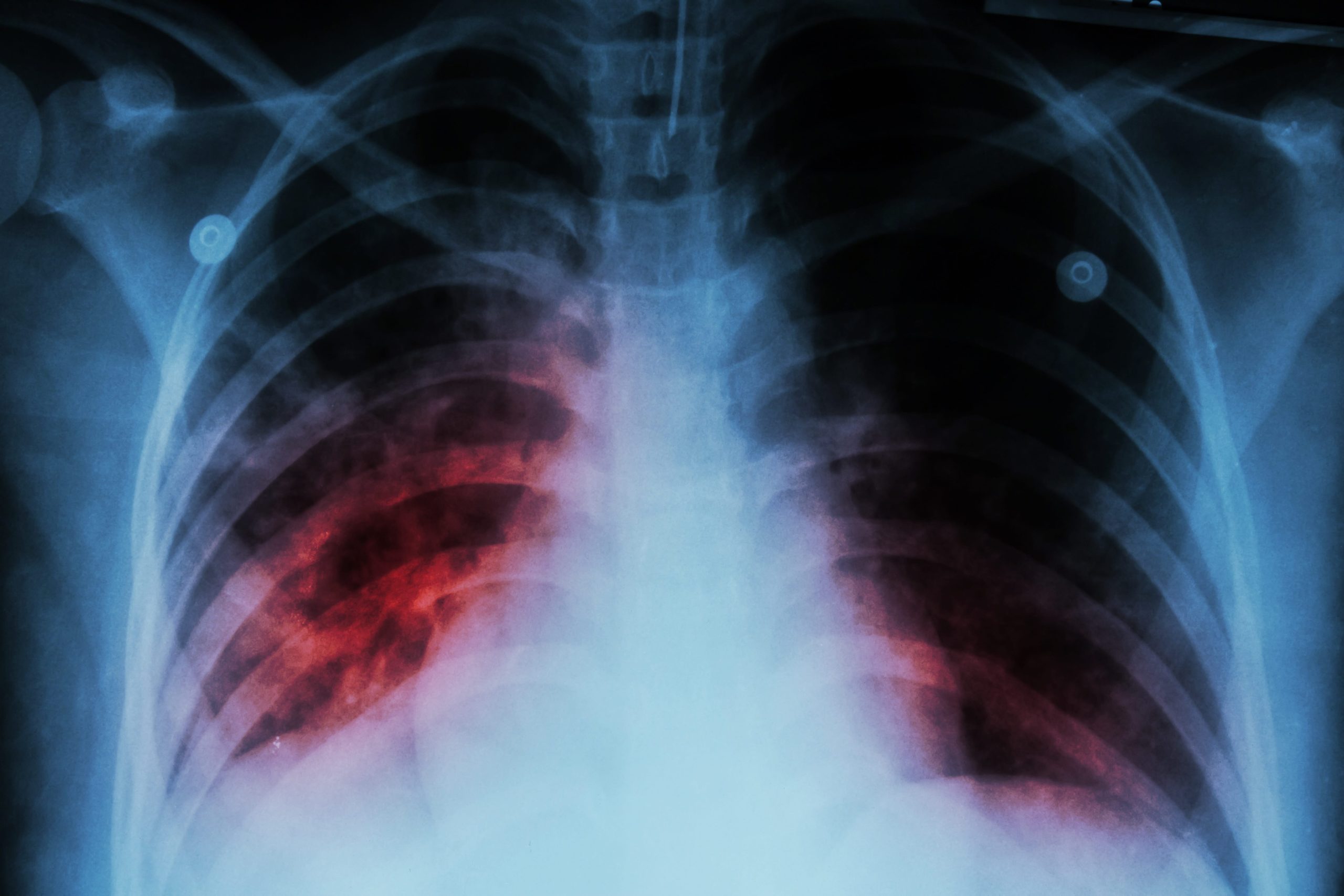
Once a widespread killer, tuberculosis has been reduced to a rarity in the United States, thanks to advances in antibiotics and infectious disease control. But it’s still virulent overseas. And sometimes, it hits home.
A recent outbreak of the illness in southern Minnesota has been traced to Mankato State University. At least eight people associated with the university have come down with active infections, and another 30 have been identified as latent carriers (meaning they tested positive for it but haven’t developed any symptoms and aren’t contagious). The state Health Department is warning that anyone who has been on campus since August 2016 should pay attention to respiratory symptoms that could indicate an infection.
What is TB and why is it dangerous?
Tuberculosis is lung infection caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It spreads through airborne particles from coughing and sneezing. Symptoms include:
- Persistent cough
- Chest pain
- Coughing up blood
- Weakness
- Loss of appetite
- Chills
- Fever
- Night sweats
Left untreated, an active TB infection can spread to other parts of the body, leading to serious complications or even death. While a TB vaccine is available, it’s not routinely given in the United States due to its relative ineffectiveness.
How prevalent is it?
Nationwide, only about 10,000 cases are reported every year, and a large percentage of those are among people with international ties. Globally, however, about 1.4 billion people – a quarter of the world’s population – are TB carriers, and 10 million have active infections. Americans are most at risk when travelling abroad. On international flights, close quarters and stale air create the perfect conditions for the disease to spread.
In Minnesota, though, TB outbreaks are rare. They’re a special cause for concern when they involve antibiotic-resistant strains. In 2017, a drug-resistant TB outbreak in Ramsey County killed 17 people.
A simple blood or skin test can detect the presence of TB bacteria. The best way to contain the illness is by seeking testing and treatment right away.
















